Developing Tools and FAIR Principles for the MetBase Database
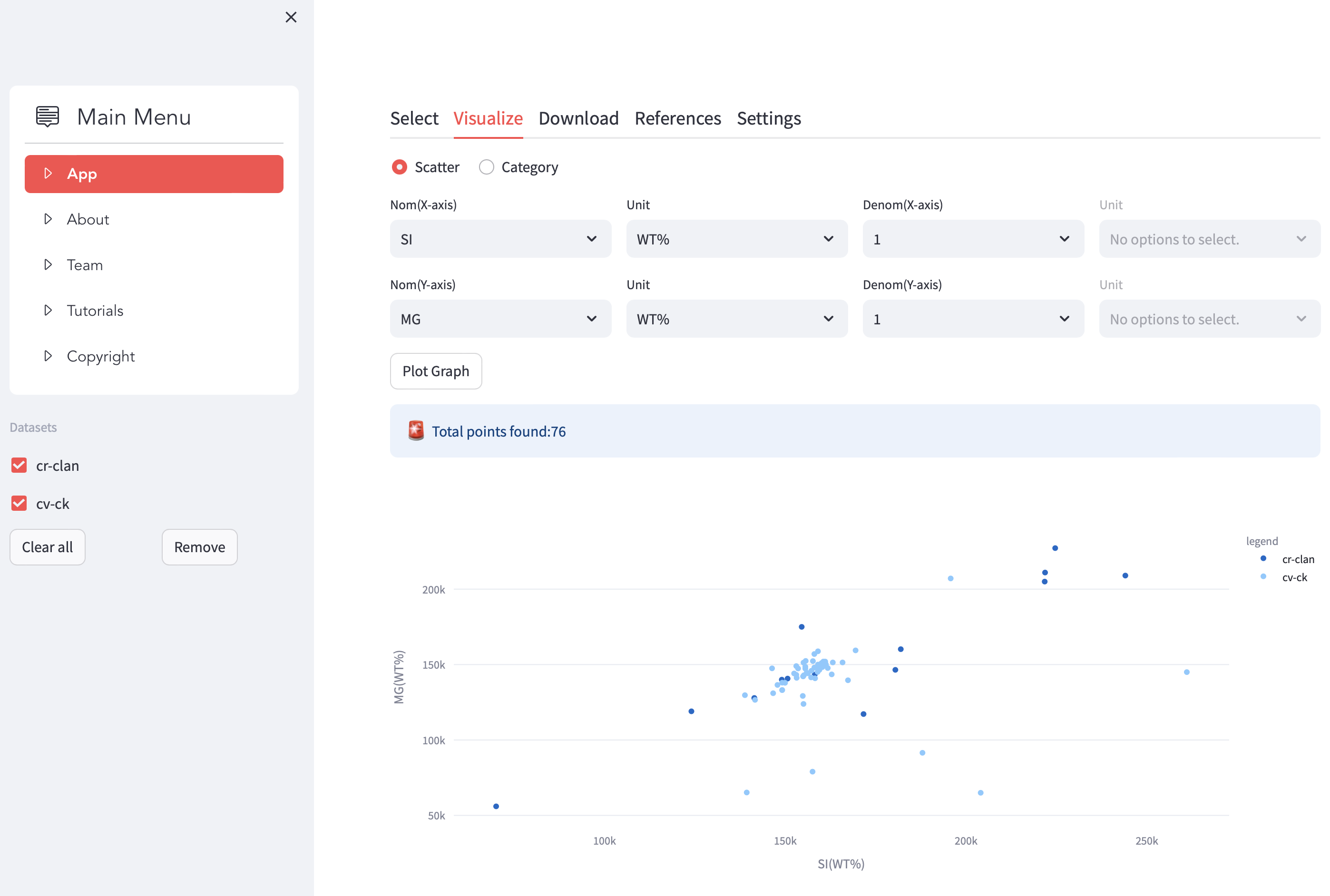
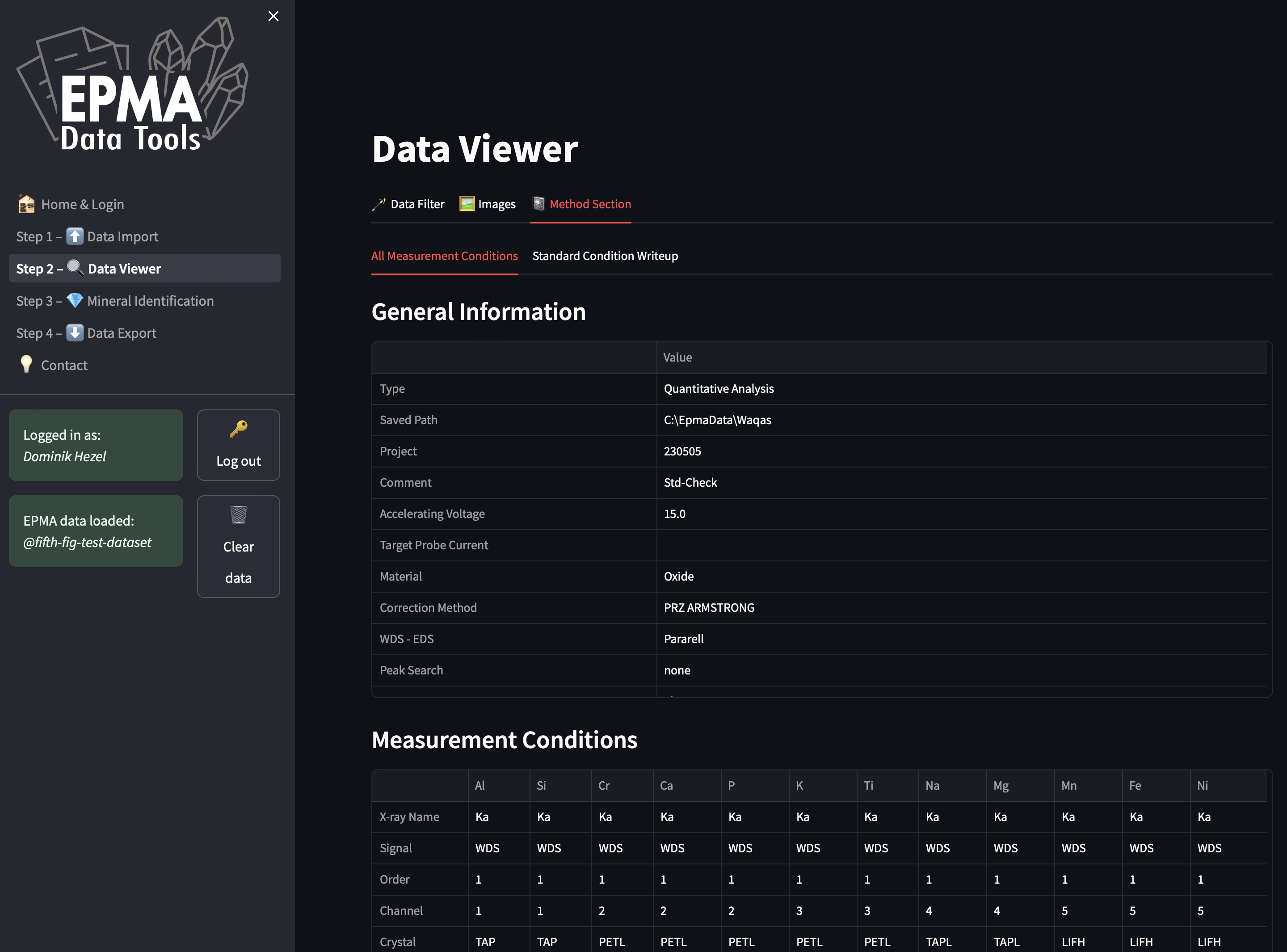
MetBase is the largest meteorite database for chemical and isotopic data which can be accessed and visualised through a web-application. MetBase has been founded more than 25 years ago and does not follow FAIR principles, while its accompanying web-app requires a significant technical and design update to become much more versatile. The database will be made FAIR, in particular to become interoperable with a new planetary materials database (Astromat), as well as the globally largest geochemical databases such as EarthChem and GEOROC, and the web-app will receive an entirely new and modular, technical foundation. MetBase will soon be successfully merged with the NASA supported Astromat database, and together with now other databases be accessible through the entirely new Data-Access Visualiser web-app (Media 1). The new EPMA Data Tools make raw data from instruments FAIR by using the Kadi4Mat electronic lab notebook and a web-app to automatically post-process the raw data before these can be accessed by researchers (Media 2).
The community highly profits from now having only one central meteorite database, access this together with other databases through a technically advanced web-app and have a solution for how instrument data can be easily made FAIR by automatically following community recommended standards and best practises. The two new apps were built and designed particularly to be expandable with new functionalities and transferable to other science domains. Communities around such apps could drive adoption through e.g., hackathons which are attractive and effective low-cost events.
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded by the German Research Foundation (NFDI4Earth, DFG project no. 460036893, https://www.nfdi4earth.de/).